Jitendra Narayan
Tag cloud
Our Sponsors
- Blogs
- Jitendra Narayan
- Tools to detect synteny blocks regions among multiple genomes
Tools to detect synteny blocks regions among multiple genomes
- Public
- 3 likes
Jit liked this 4178 days ago
Priya Singh liked this 3574 days ago
Jitendra Narayan liked this 3283 days ago
The synteny block (which etymologically means “on the same ribbon”) is a collection of contiguous genes located on the same chromosome. These block regions have mostly been preserved by genome rearrangements, and so synteny blocks from two related species (e.g., humans and mice) will be roughly similar but flipped around on the respective genomes. Ovcharenko et. al. define it as ‘any conserved sequence blocks, regardless of whether it encompasses multiple genes, an area containing single genes, or areas devoid of known genes to be considers as synteny block as long as there is conservation at the sequence level. Today, however, biologists usually refer to synteny as the conservation of blocks of order within two sets of chromosomes that are being compared with each other. This concept can also be referred to as shared synteny. The NHBLI/NCBI Glossary define synteny as “Two genes which occur on the same chromosome are syntenic; however, syntenic genes may or may not be "linked."
Now a day, geneticists have developed a language of their own. They are pouring lots of money and energy to read the entire genomic text and understand the gods own code ATGC. It is somewhat fascinating, not only for geneticist but also for non-biologist to know that there are several conserved blocks in genome which remain conserved over hundreds of millions of years. There have been several researches on conserved blocks and non-conserved regions to understand the mechanism and importance of all these regions (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2675965/. The finding indicates conservation and rearrangements of certain evolutionary important genes play an important role in evolution/adaptive changes (http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v491/n7424/abs/nature11622.html https://academic.oup.com/gbe/article/8/8/2442/2198198/Novel-Insights-into-Chromosome-Evolution-in-Birds , http://science.sciencemag.org/content/346/6215/1311.
But the puzzle remains open, how to correctly define the synteny (presence of two or more genes on the same chromosome) and conserved synteny (presence of two or more genes on chromosome of each of the two species) on several genomes.

Figure: Image generated with Evolution Highway (EH) tool http://eh-demo.ncsa.illinois.edu/
Keeping the new approach to define conserved synteny in mind there have been various algorithms developed to identify the conserved homologous synteny blocks (HSB) amongst species. Some of them which were commonly used for synteny detections are:
SyntenyTracker ( http://www-app.igb.uiuc.edu/labs/lewin/donthu/Synteny_assign/html/,
SyntenyTracker was shown to be an efficient and accurate automated tool for defining HSBs using datasets that may contain minor errors resulting from limitations in map construction methodologies.
CoGe (http://genomevolution.org/CoGe/SynFind.pl )
Satsuma (http://evomics.org/learning/genomics/satsuma/)
Cinteny (http://cinteny.cchmc.org/) ,
Cinteny server can be used for finding regions syntenic across multiple genomes and measuring the extent of genome rearrangement using reversal distance as a measure.
OrthoCluster (http://krono.act.uji.es/noticias/orthocluster-a-new-tool-for-mining-syntenic-blocks)
A new tool for mining syntenic blocks in comparative genomics
SynMap (http://genomevolution.org/wiki/index.php/SynMap,
SyMAP (http://www.symapdb.org/)
SyMAP (Synteny Mapping and Analysis Program) v4.0 is an automated system for identifying and displaying genome synteny alignments. The genomes may be represented by sequenced chromosomes (pseudomolecules), by draft sequence contigs, or by FPC physical maps (with BAC-end or marker sequence).
http://genomevolution.org/CoGe/SynMap.pl
RegionMiner (http://www.genomatix.de/online_help/help_regionminer/orthologous.html)
SyntenyMiner is being developed as an application to visualize and interrogate comparisons among multiple complete genome sequences. http://syntenyminer.sourceforge.net/
AutoGRAPH ( http://autograph.genouest.org/,
AutoGRAPH is an integrated web server for multi-species comparative genomic analysis. It is designed for constructing and visualizing synteny maps between two or three species, determination and display of macrosynteny and microsynteny relationships among species, and for highlighting evolutionary breakpoints.
SynChro(http://www.lgm.upmc.fr/CHROnicle/SynChro.html)
SynChro is a tool designed to define conserved synteny blocks. It reconstructs synteny blocks between pairwise comparison of multiple genomes. The reconstructed synteny blocks may overlap each other, be included in one another or duplicated due to micro-rearrangements.
SyntenyView ( http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/dtucourse/cookbooks/nikob/exercises/gf1_output_5.html,
Ensembl 'SyntenyView' shows conservation of large-scale gene order between species pairs. A brief summary of the calculation method appears at the bottom of this help page. The left of a 'SyntenyView' page displays a diagram of chromosomes with blocks of conserved synteny. The right of a page shows homology matches between individual genes within syntenic blocks.
SynBrowse ( http://www.synbrowse.org/,
SynBrowse (Synteny Browser) is a generic sequence comparison tool for visualizing genome alignments both within and between species. It is intended to help scientists study and analyze synteny, homologous genes and other conserved elements between sequences. This software is useful in studying genome duplication and evolution. It can also aid in identifying uncharacterized genes, putative regulatory elements and novel structural features of study species by comparing to a well annotated reference sequence, thus enabling genome curators to refine and edit annotations of species that have incomplete genome annotations.
Sibelia (http://arxiv.org/abs/1307.7941.
A comparative genomic tool: It assists biologists in analysing the genomic variations that correlate with pathogens, or the genomic changes that help microorganisms adapt in different environments. Sibelia will also be helpful for the evolutionary and genome rearrangement studies for multiple strains of microorganisms.
GSV (http://cas-bioinfo.cas.unt.edu/gsv/homepage.php)
Genome Synteny Viewer allows users to upload files which contain synteny regions between two or more genomes and interactively visualize the synteny between them. GSV also allows users to upload annotation files to visualize annotated regions in addition to synteny regions.
MicroSyn (http://www.lgm.upmc.fr/CHROnicle/SynChro.html)
MicroSyn software as a means of detecting microsynteny in adjacent genomic regions surrounding genes in gene families. MicroSyn searches for conserved, flanking colinear homologous gene pairs between two genomic fragments to determine the relationship between two members in a gene family.
SynOrth (http://synorth.genereg.net/)
Synorth [s n ôrth], named in combination of "synteny" and "ortholog", is designed for the study of evolutionary changes of genomic regulatory blocks (GRBs) in vertebrate genomes, and especially the changes following the whole-genome duplication in teleost fish, by tracing the ortholog genes gain and loss in ancient synteny blocks.
SyDiG (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21441096)
Uncovering Synteny in Distant Genomes.
MapSynteny (http://www.automatizacionysistemas.com/download.html)
MapSynteny is a macro in MS Excel® able to create images to show the relationship between genetic maps and large sequences (scaffolds, chromosomes, BACs, etc.). Based on tab – delimited BLAST results and some formulas, a suitable image of syntenic relationships or physical mapping can be obtained. http://www.automatizacionysistemas.com/Poster_MapSynteny.pdf
One of the best synteny tutorial for beginer @ http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/synteny-inferring-ancestral-genomes-44022
Reference:
http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/synteny-inferring-ancestral-genomes-44022
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v491/n7424/full/nature11622.html
- JBrowse: Embeddable genome browser built completely with JavaScript and HTML5
2810 days ago
Jitbookmark - Synima: a Synteny imaging tool for annotated genome assemblies
2687 days ago
Abhimanyu Singhbookmark - CAUSEL: an epigenome- and genome-editing pipeline for establishing function of noncoding GWAS...
2526 days ago
BioJokerbookmark - Cogent: a tool for reconstructing the coding genome using high-quality full-length transcriptome...
2456 days ago
Jitbookmark - Biological databases !
2217 days ago
BioStarbookmark - Murasaki
3447 days ago
Anjanabookmark - Synteny Portal: a web-based application portal for synteny block analysis
3211 days ago
Jitbookmark - AirLift, a methodology and tool for comprehensively moving mappings and annotations from one genome...
2268 days ago
Jitbookmark

Comments
r2cat (related reference based contig arrangement tool) can be used to order a set of contigs with respect to a single reference genome. This is done by mapping the contigs onto the reference using a q-gram filter. The mapping is visualized in a synteny plot. Find more at http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/cg-cat/r2cat.html
Thanks for such an informative blog. I notice MCScan is missing. MCScan is an algorithm able to scan multiple genomes or subgenomes in order to identify putative homologous chromosomal regions, and align these regions using genes as anchors. More at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22217600
i-ADHoRe is a highly sensitive software tool to detect degenerated homology relations within and between different genomes.
Thanks for such a useful content. I found this online "Incorrect use of the term synteny" hope useful http://www.nature.com/scitable/content/Incorrect-use-of-the-term-synteny-17320
A formal definition for syntenic blocks https://www1.ethz.ch/bsse/cbg/news/ascona2013/posters/Ghiurcuta.pdf
A Fugu–Human Genome Synteny Viewer: web software for graphical display and annotation reports of synteny between Fugu genomic sequence and human genes http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/32/8/2618.short
Orthology Detection Combining Clustering and Synteny for Very Large Datasets http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0105015
Thanks for such a useful list of synteny identification tools. If anyone interested to analyze synteny at the protein level, they can try this tool https://github.com/thiesgehrmann/proteny
Check out the new addition of synteny detection tool SimpleSynteny http://www.dveltri.com/simplesynteny/
Gbrowse synteny visualization http://www.gmod.org/wiki/GBrowse_syn_Tutorial
For bacterial synteny -- MicroScope: Microbial Genome Annotation & Analysis Platform @ https://www.genoscope.cns.fr/agc/microscope/home/index.php
Useful bacterial gene synteny explorer @ http://archaea.u-psud.fr/synttax/ and http://archaea.u-psud.fr/absynte/
Rapid pair-wise synteny analysis of large bacterial genomes using web-based GeneOrder4.0 @ http://binf.gmu.edu:8080/GeneOrder4.0/
R package to Finds Synteny in a Sequence Database http://origin.rdrr.io/bioc/DECIPHER/man/FindSynteny.html
This synteny visualization tool is relatively new and intersting
http://cas-bioinfo.cas.unt.edu/mgsv/
A recently published synteny viewer "simplesynteny"
http://www.dveltri.com/simplesynteny/
It is recommended to used genomes (N50 > 1Mb) for synteny analysis https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-018-2026-4
Align Synteny - Beginning from completed or draft genomes, find shared syntenic regions and align them quickly while accounting for inversions, rearrangements, and duplications.
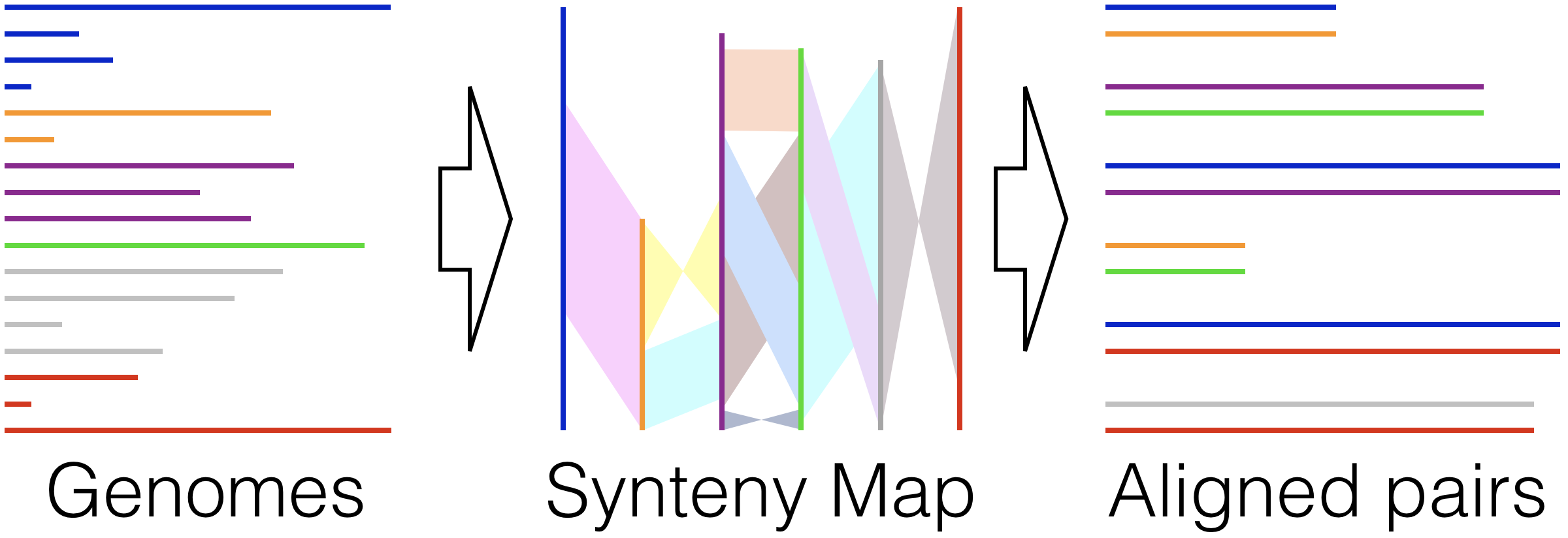
http://www2.decipher.codes/AlignSynteny.html
SynChro seems to be the fastest synteny detection tool.
http://www.lcqb.upmc.fr/CHROnicle/SynChro.html
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/5320/68e328d1aaefa435eefe679f54c018e5c2aa.pdf
The paper conclude:
SynChro is a fast, efficient and user-friendly tool to reconstruct synteny blocks between (complex) genomes harboring different levels of synteny conservation. Despite a very simple algorithm, the reconstruction is highly congruent with reconstructions obtained with more sophisticated tools.
The main advantages of SynChro are the following:
(i) it is fast (it takes, on a desk computer, on the order of 40 minutes to compare two vertebrate genomes);
(ii) it is easy to use (a unique parameter D, which is really simple to handle, needs to be set) and
(iii) it provides a rich set of graphic outputs (notably an interactive synteny map that allows zooming in breakpoint regions).
halSynteny is the latest input in computational synteny
halSynteny: a fast, easy-to-use conserved synteny block construction method for multiple whole-genome alignments
https://academic.oup.com/gigascience/article/9/6/giaa047/5848161
https://github.com/ComparativeGenomicsToolkit/hal/tree/master/synteny
Synteny based tool to arrange contigs "r2cat: synteny plots and comparative assembly" http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/r2cat
https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/26/4/570/243369
halSynteny program makes it possible to speed up the computations by over two times in comparison with SatsumaSynteny2, another popular tool. Such high efficiency was attained by implementing a mathematically effective algorithm using C++.
https://phys.org/news/2020-06-scientists-synteny-blocks-animals.html
https://github.com/ComparativeGenomicsToolkit/hal/tree/master/synteny
halSynteny: a fast, easy-to-use conserved synteny block construction method for multiple whole-genome alignments https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32463100/
Genome synteny analysis is the comparison of the genomic structure and gene content of two or more related species. Here are some general steps to follow for conducting a genome synteny analysis:
Choose the species: Select the species that you want to compare based on their evolutionary relationship or biological interest.
Obtain the genome sequences: Download the genome sequences of the selected species from a public database, such as NCBI or Ensembl.
Gene annotation: Annotate the genes in each genome using gene prediction software or tools such as MAKER.
Identify orthologous genes: Identify the orthologous genes between the genomes using tools such as OrthoFinder or OrthoMCL. Orthologous genes are genes that are homologous and have a common ancestor, but have diverged due to speciation.
Determine the synteny: Determine the synteny between the genomes by comparing the location and order of the orthologous genes. Synteny can be visualized using tools such as Circos or SynMap.
Interpret the results: Interpret the results of the synteny analysis by identifying conserved genomic regions, identifying gene families that have been lost or gained in specific lineages, and inferring the evolutionary history of the compared species.
Validate the results: Validate the results of the synteny analysis by comparing them to other sources of genomic data, such as gene expression or functional analysis.
Overall, genome synteny analysis is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of genome structure, gene content, and evolutionary relationships between species. The analysis can provide insights into the genomic evolution of species and can be used to predict the function of genes in related species.